Evaluate and Simplify Square Roots
Learning Outcomes
- Evaluate principal square roots.
- Use the product rule to simplify square roots.
A General Note: Principal Square Root
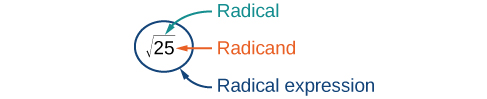
The principal square root of [latex]a[/latex] is the nonnegative number that, when multiplied by itself, equals [latex]a[/latex]. It is written as a radical expression, with a symbol called a radical over the term called the radicand: [latex]\sqrt{a}[/latex].Q & A
Does [latex]\sqrt{25}=\pm 5[/latex]?
No. Although both [latex]{5}^{2}[/latex] and [latex]{\left(-5\right)}^{2}[/latex] are [latex]25[/latex], the radical symbol implies only a nonnegative root, the principal square root. The principal square root of 25 is [latex]\sqrt{25}=5[/latex].Example: Evaluating Square Roots
Evaluate each expression.- [latex]\sqrt{100}[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{\sqrt{16}}[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{25+144}[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{49}-\sqrt{81}[/latex]
Answer:
- [latex]\sqrt{100}=10[/latex] because [latex]{10}^{2}=100[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{\sqrt{16}}=\sqrt{4}=2[/latex] because [latex]{4}^{2}=16[/latex] and [latex]{2}^{2}=4[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{25+144}=\sqrt{169}=13[/latex] because [latex]{13}^{2}=169[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{49}-\sqrt{81}=7 - 9=-2[/latex] because [latex]{7}^{2}=49[/latex] and [latex]{9}^{2}=81[/latex]
Q & A
For [latex]\sqrt{25+144}[/latex], can we find the square roots before adding?
No. [latex]\sqrt{25}+\sqrt{144}=5+12=17[/latex]. This is not equivalent to [latex]\sqrt{25+144}=13[/latex]. The order of operations requires us to add the terms in the radicand before finding the square root.Try It
Evaluate each expression.- [latex]\sqrt{225}[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{\sqrt{81}}[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{25 - 9}[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{36}+\sqrt{121}[/latex]
Answer:
- [latex]15[/latex]
- [latex]3[/latex]
- [latex]4[/latex]
- [latex]17[/latex]
Use the Product Rule to Simplify Square Roots
To simplify a square root, we rewrite it such that there are no perfect squares in the radicand. There are several properties of square roots that allow us to simplify complicated radical expressions. The first rule we will look at is the product rule for simplifying square roots, which allows us to separate the square root of a product of two numbers into the product of two separate rational expressions. For instance, we can rewrite [latex]\sqrt{15}[/latex] as [latex]\sqrt{3}\cdot \sqrt{5}[/latex]. We can also use the product rule to express the product of multiple radical expressions as a single radical expression.A General Note: The Product Rule for Simplifying Square Roots
If [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]b[/latex] are nonnegative, the square root of the product [latex]ab[/latex] is equal to the product of the square roots of [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]b[/latex].How To: Given a square root radical expression, use the product rule to simplify it.
- Factor any perfect squares from the radicand.
- Write the radical expression as a product of radical expressions.
- Simplify.
Recall Prime Factorization
It can be helpful, when simplifying square roots, to write the radicand as a product of primes in order to find perfect squares under the radical. Example. [latex]\sqrt{288} \quad=\quad \sqrt{2\cdot3^2\cdot4^2} \quad=\quad 3\cdot4\cdot \sqrt{2} \quad=\quad 12\sqrt{2}.[/latex]Example: Using the Product Rule to Simplify Square Roots
Simplify the radical expression.- [latex]\sqrt{300}[/latex]
- [latex]\sqrt{162{a}^{5}{b}^{4}}[/latex]
Answer: 1. [latex-display]\begin{align}&\sqrt{100\cdot 3} && \text{Factor perfect square from radicand}. \\ &\sqrt{100}\cdot \sqrt{3} && \text{Write radical expression as product of radical expressions}. \\ &10\sqrt{3} && \text{Simplify}. \\ \text{ }\end{align}[/latex-display] 2. [latex-display]\begin{align}&\sqrt{81{a}^{4}{b}^{4}\cdot 2a} && \text{Factor perfect square from radicand}. \\ &\sqrt{81{a}^{4}{b}^{4}}\cdot \sqrt{2a} && \text{Write radical expression as product of radical expressions}. \\ &9{a}^{2}{b}^{2}\sqrt{2a} && \text{Simplify}. \end{align}[/latex-display]
Try It
Simplify [latex]\sqrt{50{x}^{2}{y}^{3}z}[/latex].Answer: [latex]5|x||y|\sqrt{2yz}[/latex]. Notice the absolute value signs around x and y? That’s because their value must be positive!
[embed]How To: Given the product of multiple radical expressions, use the product rule to combine them into one radical expression.
- Express the product of multiple radical expressions as a single radical expression.
- Simplify.
Example: Using the Product Rule to Simplify the Product of Multiple Square Roots
Simplify the radical expression.[latex]\sqrt{12}\cdot \sqrt{3}[/latex]
Answer:
[latex]\begin{align}&\sqrt{12\cdot 3} && \text{Express the product as a single radical expression}. \\ &\sqrt{36} && \text{Simplify}. \\ &6 \end{align}[/latex]
Try It
Simplify [latex]\sqrt{50x}\cdot \sqrt{2x}[/latex] assuming [latex]x>0[/latex].Answer: [latex-display]10x[/latex-display] Because [latex]x>0[/latex], we do not need an absolute values.
[embed]Using the Quotient Rule to Simplify Square Roots
Just as we can rewrite the square root of a product as a product of square roots, so too can we rewrite the square root of a quotient as a quotient of square roots, using the quotient rule for simplifying square roots. It can be helpful to separate the numerator and denominator of a fraction under a radical so that we can take their square roots separately. We can rewrite [latex]\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{2}}[/latex] as [latex]\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex].A General Note: The Quotient Rule for Simplifying Square Roots
The square root of the quotient [latex]\dfrac{a}{b}[/latex] is equal to the quotient of the square roots of [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]b[/latex], where [latex]b\ne 0[/latex].How To: Given a radical expression, use the quotient rule to simplify it.
- Write the radical expression as the quotient of two radical expressions.
- Simplify the numerator and denominator.
Recall Simplifying Fractions
To simplify fractions, find common factors in the numerator and denominator that cancel.
Example: [latex]\dfrac{24}{32}\quad=\quad\dfrac{\cancel{2}\cdot\cancel{2}\cdot\cancel{2}\cdot3}{\cancel{2}\cdot\cancel{2}\cdot\cancel{2}\cdot2\cdot2}\quad=\quad\dfrac{3}{2\cdot2}\quad=\quad\dfrac{3}{4}[/latex]
Example: Using the Quotient Rule to Simplify Square Roots
Simplify the radical expression.[latex]\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{36}}[/latex]
Answer:
[latex]\begin{align}&\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{36}} && \text{Write as quotient of two radical expressions}. \\ &\frac{\sqrt{5}}{6} && \text{Simplify denominator}. \end{align}[/latex]
Try It
Simplify [latex]\sqrt{\dfrac{2{x}^{2}}{9{y}^{4}}}[/latex].Answer: [latex]\dfrac{x\sqrt{2}}{3{y}^{2}}[/latex]. We do not need the absolute value signs for [latex]{y}^{2}[/latex] because that term will always be nonnegative.
[embed]Example: Using the Quotient Rule to Simplify an Expression with Two Square Roots
Simplify the radical expression.[latex]\dfrac{\sqrt{234{x}^{11}y}}{\sqrt{26{x}^{7}y}}[/latex]
Answer:
[latex]\begin{align}&\sqrt{\frac{234{x}^{11}y}{26{x}^{7}y}} && \text{Combine numerator and denominator into one radical expression}. \\ &\sqrt{9{x}^{4}} && \text{Simplify fraction}. \\ &3{x}^{2} && \text{Simplify square root}. \end{align}[/latex]
Try It
Simplify [latex]\dfrac{\sqrt{9{a}^{5}{b}^{14}}}{\sqrt{3{a}^{4}{b}^{5}}}[/latex].Answer: [latex-display]{b}^{4}\sqrt{3ab}[/latex-display]
[embed]Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
- Simplify Square Roots With Variables. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com). License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Question ID 14119. Authored by: James Sousa. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License, CC-BY + GPL.
- Question ID 109776, 110285, 110272, 110287, 110387. Authored by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License, CC-BY + GPL.
CC licensed content, Specific attribution
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: OpenStax College Algebra. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution.

