The Ellipse
Can you imagine standing at one end of a large room and still being able to hear a whisper from a person standing at the other end? The National Statuary Hall in Washington, D.C. is such a room.[footnote]Architect of the Capitol. http://www.aoc.gov. Accessed April 15, 2014.[/footnote] It is an oval-shaped room called a whispering chamber because the shape makes it possible for sound to travel along the walls. In this section, we will investigate the shape of this room and its real-world applications, including how far apart two people in Statuary Hall can stand and still hear each other whisper. Figure 1. The National Statuary Hall in Washington, D.C. (credit: Greg Palmer, Flickr)
Figure 1. The National Statuary Hall in Washington, D.C. (credit: Greg Palmer, Flickr)Equations of Ellipses
A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines the shape.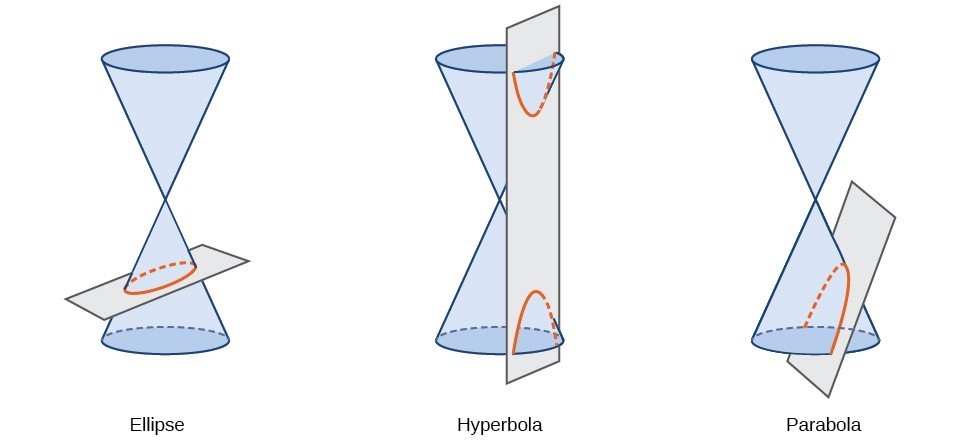 Conic sections can also be described by a set of points in the coordinate plane. Later in this chapter, we will see that the graph of any quadratic equation in two variables is a conic section. The signs of the equations and the coefficients of the variable terms determine the shape. This section focuses on the four variations of the standard form of the equation for the ellipse. An ellipse is the set of all points [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex] in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant. Each fixed point is called a focus (plural: foci).
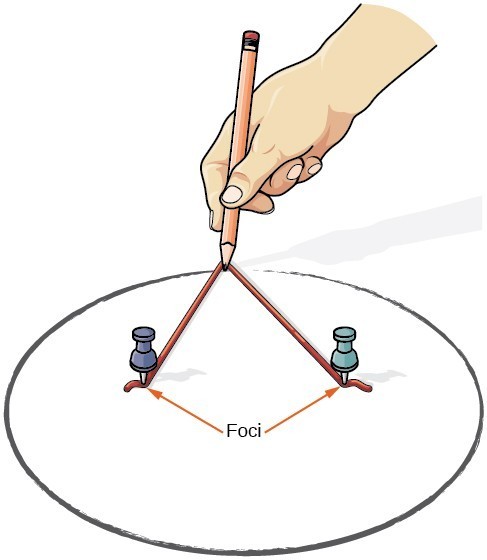
We can draw an ellipse using a piece of cardboard, two thumbtacks, a pencil, and string. Place the thumbtacks in the cardboard to form the foci of the ellipse. Cut a piece of string longer than the distance between the two thumbtacks (the length of the string represents the constant in the definition). Tack each end of the string to the cardboard, and trace a curve with a pencil held taut against the string. The result is an ellipse.
Conic sections can also be described by a set of points in the coordinate plane. Later in this chapter, we will see that the graph of any quadratic equation in two variables is a conic section. The signs of the equations and the coefficients of the variable terms determine the shape. This section focuses on the four variations of the standard form of the equation for the ellipse. An ellipse is the set of all points [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex] in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant. Each fixed point is called a focus (plural: foci).
We can draw an ellipse using a piece of cardboard, two thumbtacks, a pencil, and string. Place the thumbtacks in the cardboard to form the foci of the ellipse. Cut a piece of string longer than the distance between the two thumbtacks (the length of the string represents the constant in the definition). Tack each end of the string to the cardboard, and trace a curve with a pencil held taut against the string. The result is an ellipse.
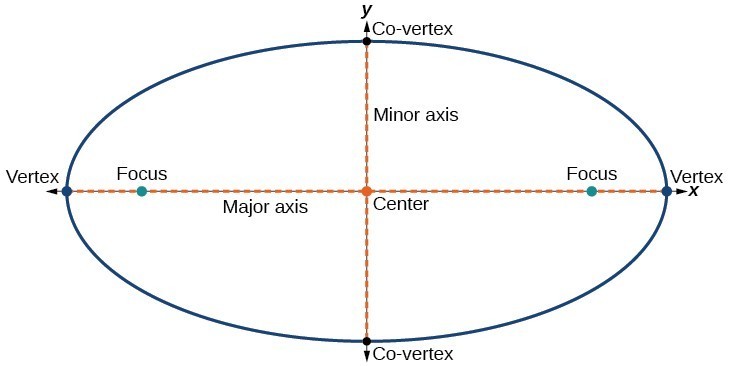
 Every ellipse has two axes of symmetry. The longer axis is called the major axis, and the shorter axis is called the minor axis. Each endpoint of the major axis is the vertex of the ellipse (plural: vertices), and each endpoint of the minor axis is a co-vertex of the ellipse. The center of an ellipse is the midpoint of both the major and minor axes. The axes are perpendicular at the center. The foci always lie on the major axis, and the sum of the distances from the foci to any point on the ellipse (the constant sum) is greater than the distance between the foci.
Every ellipse has two axes of symmetry. The longer axis is called the major axis, and the shorter axis is called the minor axis. Each endpoint of the major axis is the vertex of the ellipse (plural: vertices), and each endpoint of the minor axis is a co-vertex of the ellipse. The center of an ellipse is the midpoint of both the major and minor axes. The axes are perpendicular at the center. The foci always lie on the major axis, and the sum of the distances from the foci to any point on the ellipse (the constant sum) is greater than the distance between the foci.
 In this section, we restrict ellipses to those that are positioned vertically or horizontally in the coordinate plane. That is, the axes will either lie on or be parallel to the x- and y-axes. Later in the chapter, we will see ellipses that are rotated in the coordinate plane.
To work with horizontal and vertical ellipses in the coordinate plane, we consider two cases: those that are centered at the origin and those that are centered at a point other than the origin. First we will learn to derive the equations of ellipses, and then we will learn how to write the equations of ellipses in standard form. Later we will use what we learn to draw the graphs.
In this section, we restrict ellipses to those that are positioned vertically or horizontally in the coordinate plane. That is, the axes will either lie on or be parallel to the x- and y-axes. Later in the chapter, we will see ellipses that are rotated in the coordinate plane.
To work with horizontal and vertical ellipses in the coordinate plane, we consider two cases: those that are centered at the origin and those that are centered at a point other than the origin. First we will learn to derive the equations of ellipses, and then we will learn how to write the equations of ellipses in standard form. Later we will use what we learn to draw the graphs.
Writing Equations of Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin
Like the graphs of other equations, the graph of an ellipse can be translated. If an ellipse is translated [latex]h[/latex] units horizontally and [latex]k[/latex] units vertically, the center of the ellipse will be [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex]. This translation results in the standard form of the equation we saw previously, with [latex]x[/latex] replaced by [latex]\left(x-h\right)[/latex] and y replaced by [latex]\left(y-k\right)[/latex].A General Note: Standard Forms of the Equation of an Ellipse with Center (h, k)
The standard form of the equation of an ellipse with center [latex]\left(h,\text{ }k\right)[/latex] and major axis parallel to the x-axis is[latex]\frac{{\left(x-h\right)}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}+\frac{{\left(y-k\right)}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}=1[/latex]
where- [latex]a>b[/latex]
- the length of the major axis is [latex]2a[/latex]
- the coordinates of the vertices are [latex]\left(h\pm a,k\right)[/latex]
- the length of the minor axis is [latex]2b[/latex]
- the coordinates of the co-vertices are [latex]\left(h,k\pm b\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the foci are [latex]\left(h\pm c,k\right)[/latex], where [latex]{c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}[/latex].
[latex]\frac{{\left(x-h\right)}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{\left(y-k\right)}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1[/latex]
where- [latex]a>b[/latex]
- the length of the major axis is [latex]2a[/latex]
- the coordinates of the vertices are [latex]\left(h,k\pm a\right)[/latex]
- the length of the minor axis is [latex]2b[/latex]
- the coordinates of the co-vertices are [latex]\left(h\pm b,k\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the foci are [latex]\left(h,k\pm c\right)[/latex], where [latex]{c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}[/latex].
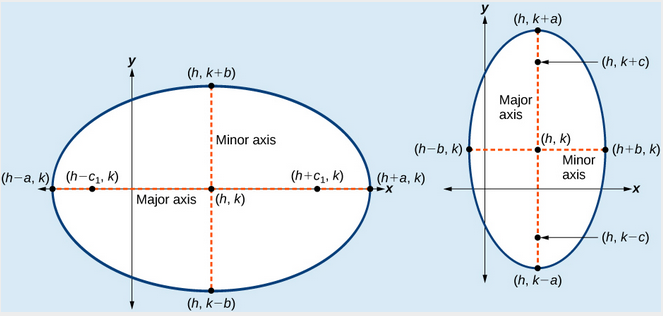 (a) Horizontal ellipse with center [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex] (b) Vertical ellipse with center [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex]
(a) Horizontal ellipse with center [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex] (b) Vertical ellipse with center [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex]How To: Given the vertices and foci of an ellipse not centered at the origin, write its equation in standard form.
- Determine whether the major axis is parallel to the x- or y-axis.
- If the y-coordinates of the given vertices and foci are the same, then the major axis is parallel to the x-axis. Use the standard form [latex]\frac{{\left(x-h\right)}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}+\frac{{\left(y-k\right)}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}=1[/latex].
- If the x-coordinates of the given vertices and foci are the same, then the major axis is parallel to the y-axis. Use the standard form [latex]\frac{{\left(x-h\right)}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{\left(y-k\right)}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1[/latex].
- Identify the center of the ellipse [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex] using the midpoint formula and the given coordinates for the vertices.
- Find [latex]{a}^{2}[/latex] by solving for the length of the major axis, [latex]2a[/latex], which is the distance between the given vertices.
- Find [latex]{c}^{2}[/latex] using [latex]h[/latex] and [latex]k[/latex], found in Step 2, along with the given coordinates for the foci.
- Solve for [latex]{b}^{2}[/latex] using the equation [latex]{c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}[/latex].
- Substitute the values for [latex]h,k,{a}^{2}[/latex], and [latex]{b}^{2}[/latex] into the standard form of the equation determined in Step 1.
Example: Writing the Equation of an Ellipse Centered at a Point Other Than the Origin
What is the standard form equation of the ellipse that has vertices [latex]\left(-2,-8\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(-2,\text{2}\right)[/latex] and foci [latex]\left(-2,-7\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(-2,\text{1}\right)?[/latex]Answer: The x-coordinates of the vertices and foci are the same, so the major axis is parallel to the y-axis. Thus, the equation of the ellipse will have the form
[latex]\frac{{\left(x-h\right)}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{\left(y-k\right)}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1[/latex]
First, we identify the center, [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex]. The center is halfway between the vertices, [latex]\left(-2,-8\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(-2,\text{2}\right)[/latex]. Applying the midpoint formula, we have:[latex]\begin{array}{l}\left(h,k\right)=\left(\frac{-2+\left(-2\right)}{2},\frac{-8+2}{2}\right)\hfill \\ \text{ }=\left(-2,-3\right)\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Next, we find [latex]{a}^{2}[/latex]. The length of the major axis, [latex]2a[/latex], is bounded by the vertices. We solve for [latex]a[/latex] by finding the distance between the y-coordinates of the vertices.[latex]\begin{array}{c}2a=2-\left(-8\right)\\ 2a=10\\ a=5\end{array}[/latex]
So [latex]{a}^{2}=25[/latex]. Now we find [latex]{c}^{2}[/latex]. The foci are given by [latex]\left(h,k\pm c\right)[/latex]. So, [latex]\left(h,k-c\right)=\left(-2,-7\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(h,k+c\right)=\left(-2,\text{1}\right)[/latex]. We substitute [latex]k=-3[/latex] using either of these points to solve for [latex]c[/latex].[latex]\begin{array}{c}k+c=1\\ -3+c=1\\ c=4\end{array}[/latex] So [latex]{c}^{2}=16[/latex].
Next, we solve for [latex]{b}^{2}[/latex] using the equation [latex]{c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}[/latex].[latex]\begin{array}{c}{c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}\\ 16=25-{b}^{2}\\ {b}^{2}=9\end{array}[/latex]
Finally, we substitute the values found for [latex]h,k,{a}^{2}[/latex], and [latex]{b}^{2}[/latex] into the standard form equation for an ellipse:[latex]\frac{{\left(x+2\right)}^{2}}{9}+\frac{{\left(y+3\right)}^{2}}{25}=1[/latex]
Try It
What is the standard form equation of the ellipse that has vertices [latex]\left(-3,3\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(5,3\right)[/latex] and foci [latex]\left(1 - 2\sqrt{3},3\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(1+2\sqrt{3},3\right)?[/latex]Answer: [latex]\frac{{\left(x - 1\right)}^{2}}{16}+\frac{{\left(y - 3\right)}^{2}}{4}=1[/latex]
Graphs of Ellipses
Just as we can write the equation for an ellipse given its graph, we can graph an ellipse given its equation. To graph ellipses centered at the origin, we use the standard form [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}=1,\text{ }a>b[/latex] for horizontal ellipses and [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1,\text{ }a>b[/latex] for vertical ellipses.How To: Given the standard form of an equation for an ellipse centered at [latex]\left(0,0\right)[/latex], sketch the graph.
- Use the standard forms of the equations of an ellipse to determine the major axis, vertices, co-vertices, and foci.
- If the equation is in the form [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}=1[/latex], where [latex]a>b[/latex], then
- the major axis is the x-axis
- the coordinates of the vertices are [latex]\left(\pm a,0\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the co-vertices are [latex]\left(0,\pm b\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the foci are [latex]\left(\pm c,0\right)[/latex]
- If the equation is in the form [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1[/latex], where [latex]a>b[/latex], then
- the major axis is the y-axis
- the coordinates of the vertices are [latex]\left(0,\pm a\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the co-vertices are [latex]\left(\pm b,0\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the foci are [latex]\left(0,\pm c\right)[/latex]
- If the equation is in the form [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}=1[/latex], where [latex]a>b[/latex], then
- Solve for [latex]c[/latex] using the equation [latex]{c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}[/latex].
- Plot the center, vertices, co-vertices, and foci in the coordinate plane, and draw a smooth curve to form the ellipse.
Example: Graphing an Ellipse Centered at the Origin
Graph the ellipse given by the equation, [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{9}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{25}=1[/latex]. Identify and label the center, vertices, co-vertices, and foci.Answer: First, we determine the position of the major axis. Because [latex]25>9[/latex], the major axis is on the y-axis. Therefore, the equation is in the form [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1[/latex], where [latex]{b}^{2}=9[/latex] and [latex]{a}^{2}=25[/latex]. It follows that:
- the center of the ellipse is [latex]\left(0,0\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the vertices are [latex]\left(0,\pm a\right)=\left(0,\pm \sqrt{25}\right)=\left(0,\pm 5\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the co-vertices are [latex]\left(\pm b,0\right)=\left(\pm \sqrt{9},0\right)=\left(\pm 3,0\right)[/latex]
- the coordinates of the foci are [latex]\left(0,\pm c\right)[/latex], where [latex]{c}^{2}={a}^{2}-{b}^{2}[/latex] Solving for [latex]c[/latex], we have:
[latex]\begin{array}{l}c=\pm \sqrt{{a}^{2}-{b}^{2}}\hfill \\ =\pm \sqrt{25 - 9}\hfill \\ =\pm \sqrt{16}\hfill \\ =\pm 4\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Therefore, the coordinates of the foci are [latex]\left(0,\pm 4\right)[/latex]. Next, we plot and label the center, vertices, co-vertices, and foci, and draw a smooth curve to form the ellipse.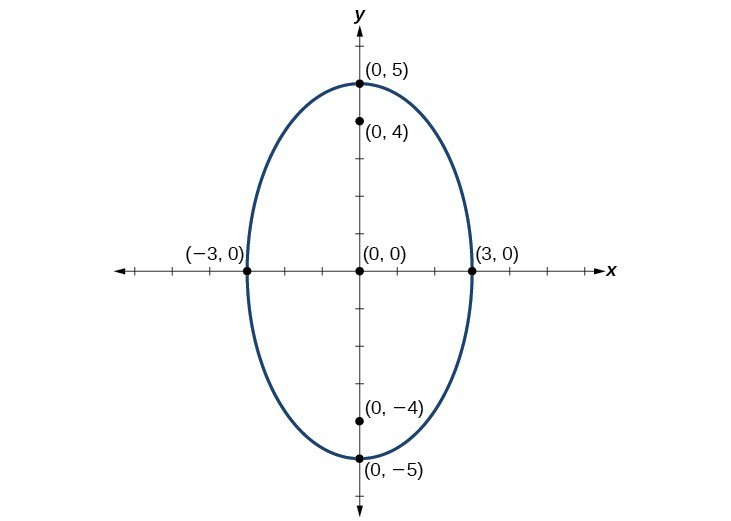
Try It
Graph the ellipse given by the equation [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{36}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{4}=1[/latex]. Identify and label the center, vertices, co-vertices, and foci.Answer:
center: [latex]\left(0,0\right)[/latex]; vertices: [latex]\left(\pm 6,0\right)[/latex]; co-vertices: [latex]\left(0,\pm 2\right)[/latex]; foci: [latex]\left(\pm 4\sqrt{2},0\right)[/latex]

Key Equations
| Horizontal ellipse, center at origin | [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}=1,\text{ }a>b[/latex] |
| Vertical ellipse, center at origin | [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{y}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1,\text{ }a>b[/latex] |
| Horizontal ellipse, center [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex] | [latex]\frac{{\left(x-h\right)}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}+\frac{{\left(y-k\right)}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}=1,\text{ }a>b[/latex] |
| Vertical ellipse, center [latex]\left(h,k\right)[/latex] | [latex]\frac{{\left(x-h\right)}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}+\frac{{\left(y-k\right)}^{2}}{{a}^{2}}=1,\text{ }a>b[/latex] |
Key Concepts
- An ellipse is the set of all points [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex] in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant. Each fixed point is called a focus (plural: foci).
- When given the coordinates of the foci and vertices of an ellipse, we can write the equation of the ellipse in standard form.
- When given an equation for an ellipse centered at the origin in standard form, we can identify its vertices, co-vertices, foci, and the lengths and positions of the major and minor axes in order to graph the ellipse.
- When given the equation for an ellipse centered at some point other than the origin, we can identify its key features and graph the ellipse.
- Real-world situations can be modeled using the standard equations of ellipses and then evaluated to find key features, such as lengths of axes and distance between foci.
Glossary
center of an ellipse the midpoint of both the major and minor axes conic section any shape resulting from the intersection of a right circular cone with a plane ellipse the set of all points [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex] in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant foci plural of focus focus (of an ellipse) one of the two fixed points on the major axis of an ellipse such that the sum of the distances from these points to any point [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex] on the ellipse is a constant major axis the longer of the two axes of an ellipse minor axis the shorter of the two axes of an ellipseLicenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
- Question ID 1667. Authored by: WebWork-Rochester. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
- Question ID 87055, 23514. Authored by: Roy Shahbazian. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
CC licensed content, Specific attribution
- Precalculus. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution.

